Mind Map
Visualize concept relationships and see the big picture of your notes
Mind maps transform your notes into visual concept maps, showing how ideas connect and relate. Perfect for visual learners and understanding complex topics, mind maps reveal the structure and relationships that might be hidden in linear text.
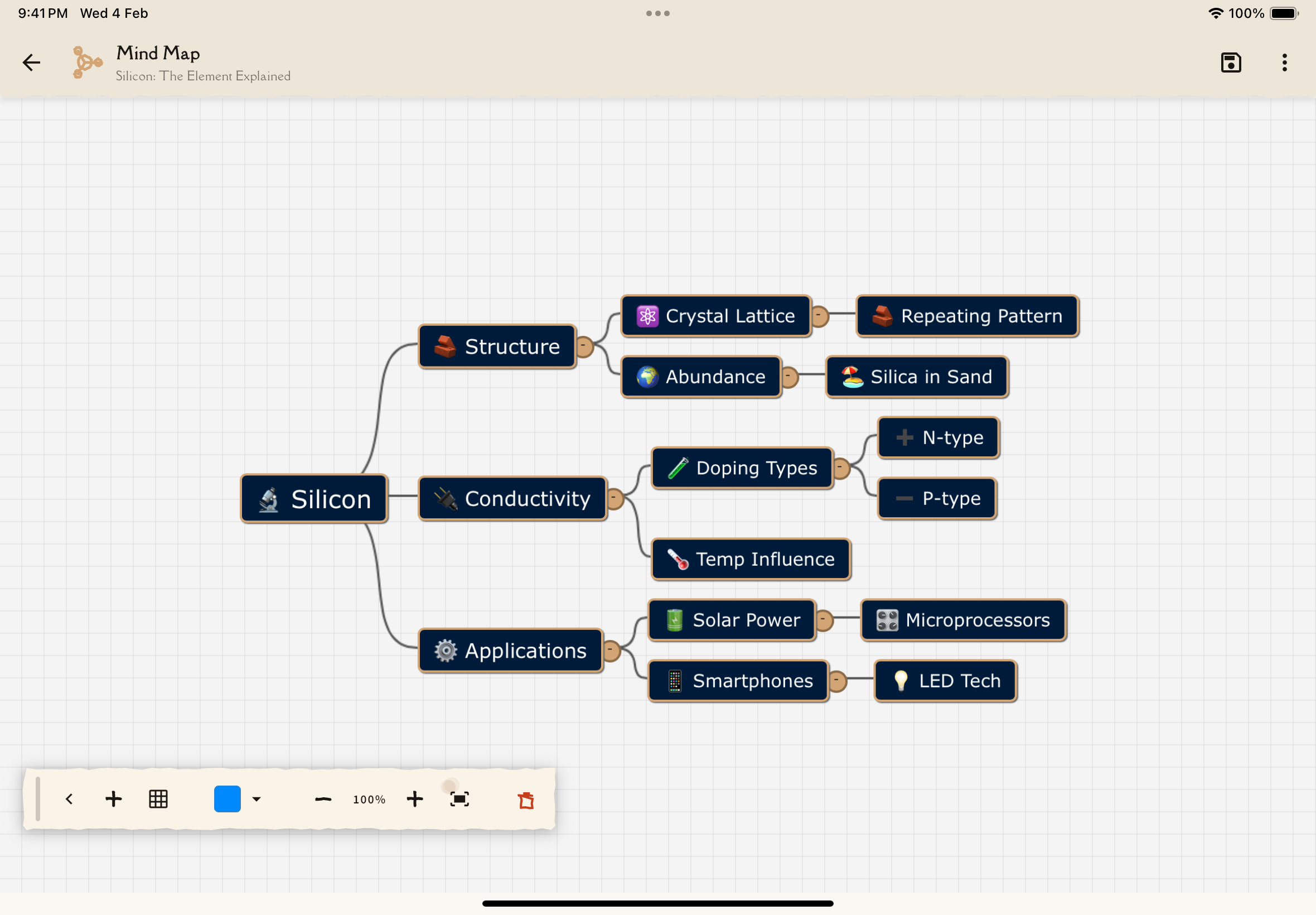
What is a Mind Map?
A mind map is a visual diagram that represents information hierarchically:
- Central node: Main topic at the center
- Branches: Major subtopics radiating outward
- Sub-branches: Details extending from subtopics
- Connections: Lines showing relationships between concepts
AI automatically generates mind maps from your notes, organizing concepts based on their relationships and importance.
Mind maps are incredible for exam prep! They help you see the "big picture" and understand how everything fits together—essential for essay questions and comprehensive exams.
Accessing the Mind Map
Navigate to any note from the Notes tab.
Tap the Study Tools tab.
Select the Mind Map card. The interactive map loads.
Understanding the Mind Map
Node Types
Central Node (largest):
- The main subject of your note
- Positioned in the center
- Usually the note title or overarching concept
Primary Nodes (large):
- Major topics or sections
- Branch directly from the central node
- Represent main ideas
Secondary Nodes (medium):
- Subtopics and key concepts
- Branch from primary nodes
- Provide details and examples
Tertiary Nodes (small):
- Specific facts, definitions, examples
- Branch from secondary nodes
- Fine-grained details
Visual Elements
Node Colors:
- Different colors for different topic categories
- Helps visually group related concepts
- Can customize color scheme in settings
Connection Lines:
- Solid lines: Direct hierarchical relationships (parent-child)
- Dashed lines: Cross-references (related but not hierarchical)
- Thick lines: Strong relationships
- Thin lines: Weaker or supporting relationships
Node Shapes:
- Circles: Concepts/topics
- Rounded rectangles: Definitions
- Diamonds: Key points or questions
- Rectangles: Examples or applications
Interacting with the Mind Map
Navigation
Zoom:
- Pinch gesture: Zoom in/out
- Zoom buttons: +/- buttons in corner
- Double-tap node: Zoom to focus on that branch
Pan:
- Drag gesture: Move around the map
- Two-finger drag: Faster panning
Reset View:
- Fit to screen button: Return to full map view
- Shows all nodes at optimal zoom
Node Interaction
Tap a node to:
- View full text (if abbreviated)
- See related flashcards
- Jump to that section in the Reading tab
- View linked concepts
- Access quick actions menu
Long-press a node to:
- Add personal notes to this concept
- Create flashcard from this node
- Mark as "mastered" or "needs review"
- Share this concept
- Collapse/expand branch
Swipe on node (some devices):
- Swipe up: Show related nodes
- Swipe down: Hide sub-branches
Filtering and Focus
Filter by mastery:
- Show only weak concepts (red nodes)
- Show only mastered concepts (green nodes)
- Show all (default)
Filter by type:
- Definitions only
- Examples only
- Key concepts only
- All types
Focus mode:
- Tap a node and select "Focus"
- Map shows only that branch
- Reduces clutter for complex maps
Mind maps for long notes can have 50+ nodes! Use filtering and focus mode to avoid overwhelm. Start with the big picture, then drill down into specific branches.
Using Mind Maps for Study
Strategy 1: Big Picture First
Start with all nodes visible at zoom level that shows everything.
Look at primary nodes. These are your main topics.
Follow the connections. How do topics relate?
Notice anything missing? Concepts you don't recognize? Mark them.
Zoom in on branches you need to study more deeply.
Strategy 2: Test Your Mental Model
Without looking, try to recreate it mentally or on paper.
Sketch the central topic, major branches, and connections.
Open the mind map and compare. What did you miss?
Use the Reading tab or Q&A to learn what you couldn't recall.
Repeat this exercise to build stronger mental models.
Strategy 3: Connection Discovery
Choose any two nodes that seem unrelated.
Trace the connections between them. How do they relate?
Can you articulate why they're linked? Use Q&A if unsure.
Are there relationships the map doesn't show? Add notes about them.
This builds deeper understanding beyond surface-level memorization.
Mind Map Features
Search
Find concepts quickly:
- Tap the search icon
- Type a keyword
- Matching nodes highlight
- Tap result to jump to that node
Perfect for large maps with many nodes.
Export
Share or save your mind map:
Export as Image:
- PNG or JPG format
- Include in study guides or presentations
- Share with study partners
Export as Text Outline:
- Hierarchical bullet list
- Copy to notes or other apps
Export to Mind Mapping Software:
- FreeMind format (.mm)
- XMind format
- MindManager format
Customization (Premium)
Visual Styling:
- Change color scheme (pastel, vibrant, monochrome)
- Adjust node sizes
- Modify font sizes
- Change connection line styles
Layout Options:
- Radial (default): Branches spread out from center
- Tree: Top-down hierarchical layout
- Organic: Free-form, AI-optimized spacing
Content Options:
- Show/hide node icons
- Show/hide secondary details
- Abbreviate long text or show full
Combining Mind Maps with Other Tools
Mind Map + Reading
Use the mind map as a navigation tool:
- View the map to see structure
- Tap a node you want to study
- Jump to Reading tab at that section
- Read in detail
- Return to map to navigate to next topic
This gives you context (map) and depth (reading) simultaneously.
Mind Map + Flashcards
Understand before memorizing:
- Use mind map to understand relationships
- Switch to flashcards to drill details
- When stuck, return to map to see context
- Memorization is easier with structure in mind
Mind Map + Q&A
Clarify connections:
- Notice a confusing connection in the map
- Open Q&A and ask: "How does [concept A] relate to [concept B]?"
- AI explains the relationship
- Return to map with better understanding
Mind Map + Quizzes
Test structural knowledge:
After studying the map:
- Take a quiz to test recall
- Wrong answers often reveal structural misunderstandings
- Return to map to fix mental model
- Retake quiz to verify improvement
Tips for Effective Mind Map Use
Mind map best practices:
- Start with overview: Get the big picture before diving into details
- Follow natural paths: Let your eye follow branches that interest you
- Color code personally: Add your own colors for categories that make sense to you
- Print it out: For exams, print and annotate by hand
- Recreate from memory: Best test of understanding
- Connect notes: Look for connections between multiple note maps
- Use for essays: Plan essay structure using map hierarchy
- Teaching tool: Explain the map to someone else—ultimate mastery
- Update regularly: As you learn more, mental models evolve
- Combine with linear notes: Map = structure, text = details—both matter
Common Mind Map Patterns
Different subjects create different map structures:
History Notes: Timeline-based, event nodes with cause-effect connections
Science Notes: Central theory with evidence branches, application sub-branches
Programming Notes: Language features branch into syntax, examples, use cases
Literature Notes: Themes, characters, plot points interconnect complexly
Math Notes: Formulas branch into variables, applications, example problems
Recognizing these patterns helps you navigate maps more intuitively.
What's Next?
Explore other study tools:
Or continue your study journey:
See the big picture, understand the details!